Variable Orifice Valves
Improved Safety and Reliability of Flue Gas Systems with Variable Orifice Valves.
In today’s modern refineries, the need to achieve pressure control is available by the use of variable orifice valves in lieu of conventional orifice chambers. The disadvantage of fixed orifices is that pressure control and/or sound attenuation is achieved only at a constant flow rate. However, since refineries operating conditions are seldom uniform and therefore experience variable internal flow rates and pressure fluctuations, a variable orifice design is highly advantageous to accomplish optimum results.
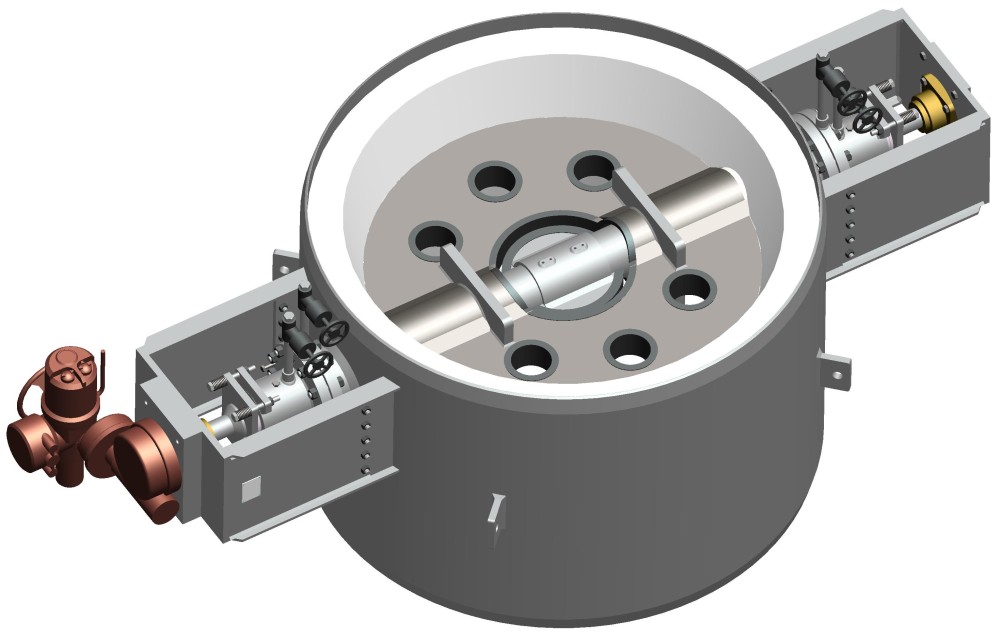

TapcoEnpro’s Approach
- Provide a valve system to replace the orifice chamber that provides reliability to the flue gas system regardless of the process flowing conditions.
- Provide a valve system to increase safety to the overall operability of the FCCU
- Provide a flue gas valve system to control the velocities to eliminate sonic velocities which is a major cause of equipment failure and erosion issues
- Provide a valve that will control the flue gas pressure reduction process in all flowing process conditions to maintain constant Delta P across the equipment
Three Valve System (DDFG plus 2 VOV)
| Inlet Pressure, psig | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature ºF | 1450 | 1400 | 1350 | 1300 | 1450 | 1400 | 1350 | 1300 | 1450 | 1400 | 1350 | 1300 |
| Flowing Velocity, fps | 1600 | 1579 | 1558 | 1536 | 1690 | 1667 | 1645 | 1622 | 1768 | 1745 | 1721 | 1697 |
| Sonic Velocity, fps | 2056 | 2029 | 2001 | 1974 | 2056 | 2029 | 2001 | 1974 | 2056 | 2029 | 2001 | 1974 |
| 1st DP, psi | 13.162 | 13.162 | 13.162 | 13.162 | 15.582 | 15.582 | 15.582 | 15.582 | 18.619 | 18.619 | 18.619 | 18.619 |
| 2nd DP, psi | 9.286 | 9.286 | 9.286 | 9.286 | 10.796 | 10.796 | 10.796 | 10.796 | 12.281 | 12.281 | 12.281 | 12.281 |
| 3rd DP, psi | 7.552 | 7.552 | 7.552 | 7.552 | 7.352 | 7.352 | 7.352 | 7.352 | 8.1 | 8.1 | 8.1 | 8.1 |
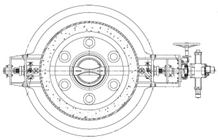
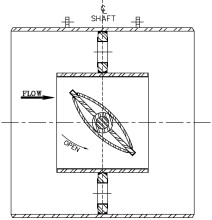
The variable orifice valve will adjust it’s flapper (disc) to close more so that the flow through the outer fixed orifice plate holes will remain constant. The delta p through the outer fixed holes will remain constant therefore the velocities through these holes will remain below sonic conditions
